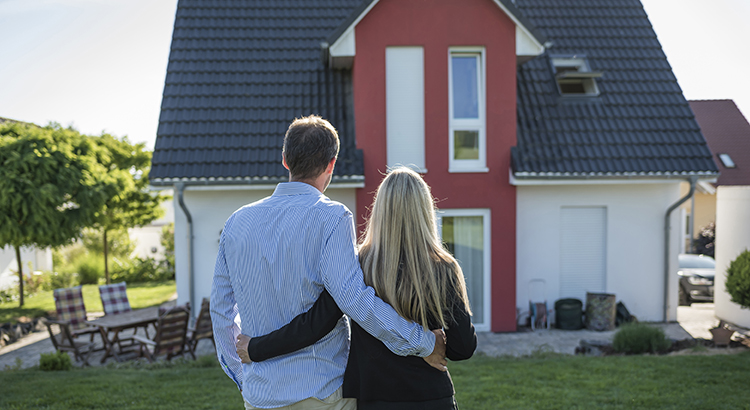
Perspective Matters When Selling Your Home or Cabin on Mt. Hood
Does the latest news about the housing market have you questioning your plans to sell your house? If so, perspective is key. Here are some of the ways a trusted real estate professional can explain the shift that’s happening today and why it’s still a sellers’ market even during the cooldown.
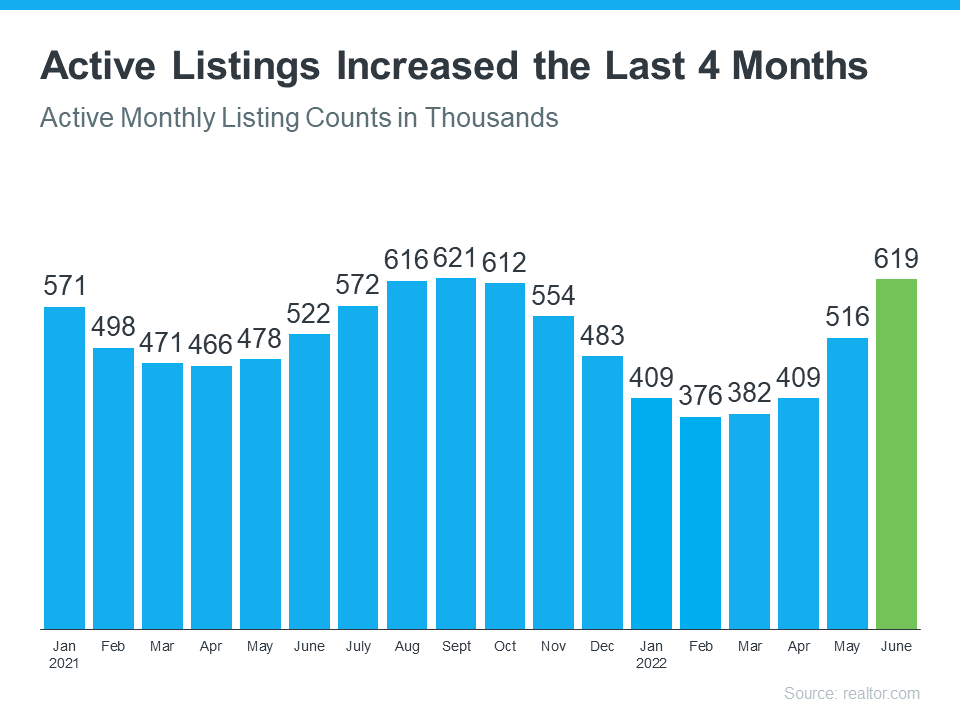
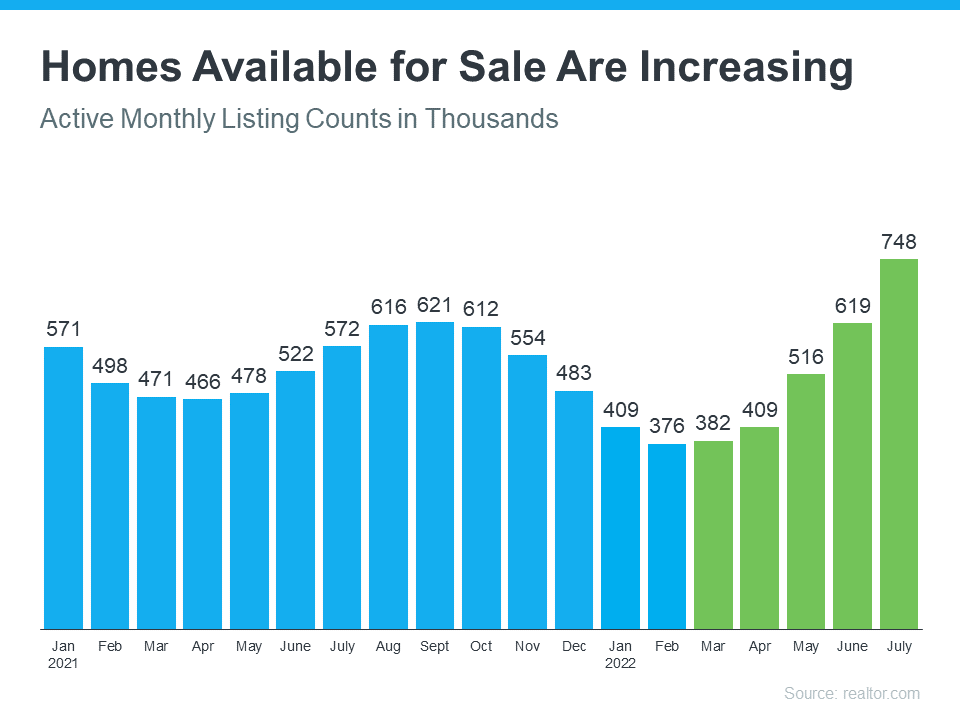
Fewer Homes for Sale than Pre-Pandemic
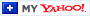
While the supply of homes available for sale has increased this year compared to last, we’re still nowhere near what’s considered a balanced market. A recent article from Calculated Risk helps put this year’s increased inventory into context (see graph below):
It shows supply this year has surpassed 2021 levels by over 30%. But the further back you look, the more you’ll understand the big picture. Compared to 2020, we’re just barely above the level of inventory we saw then. And if you go all the way back to 2019, the last normal year in real estate, we’re roughly 40% below the housing supply we had at that time.
Why does this matter to you? When inventory is low, there is still demand for your house because there just aren’t enough homes available for sale.
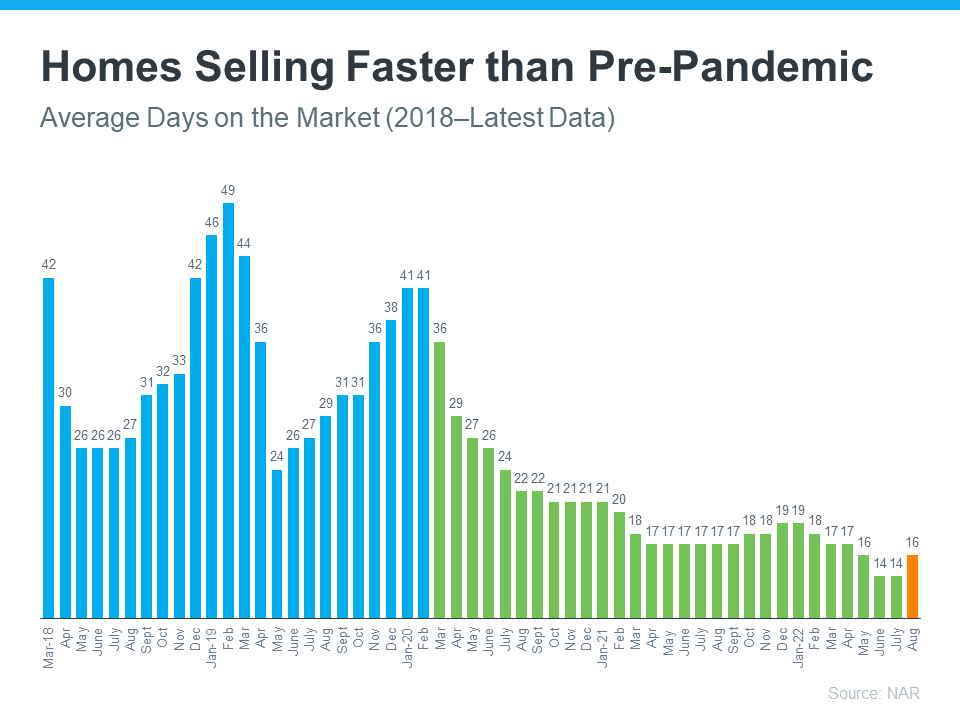
Homes Are Still Selling Faster Than More Normal Years
And while homes aren’t selling as quickly as they did a few months ago, the average number of days on the market is still well below pre-pandemic norms – in large part because inventory is so low. The graph below uses data from the Realtors’ Confidence Index by the National Association of Realtors (NAR) to illustrate this trend:
As the graph shows, the pre-pandemic numbers (shown in blue) are higher than the numbers we saw during the pandemic (shown in green). That’s because the average days on the market started to decrease as homes sold at record pace during the pandemic. Most recently, due to the cooldown in the housing market, the average days on the market have started to tick back up slightly (shown in orange) but are still far below the pre-pandemic norm.
What does this mean for you? While it may not be as fast as it was a couple of months ago, homes are still selling much faster than they did in more normal, pre-pandemic years. And if you price it right, your home could still go under contract quickly.
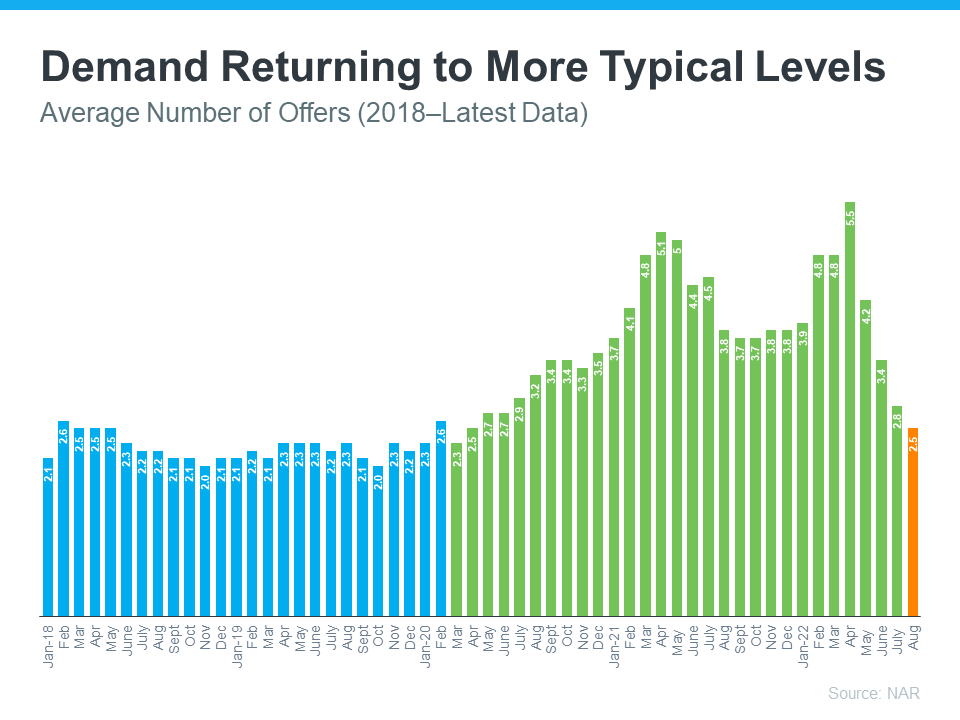
Buyer Demand Has Moderated and Is Now in Line with More Typical Years
Buyer demand has softened this year in response to rising mortgage rates. But again, perspective is key. Getting 3-5 offers like sellers did during the pandemic isn’t the norm. The graph below uses data from NAR going back to 2018 to help tell the story of this shift over time (see graph below):
Prior to the pandemic, it was typical for homes sold to see roughly 2-2.5 offers (shown in blue). As the market heated up during the pandemic, the average number of offers skyrocketed as record-low mortgage rates drove up demand (shown in green). But most recently, the number of offers on homes sold today (shown in orange) has started to return to pre-pandemic levels as the market cools from the frenzy.
What’s the takeaway for you? Buyer demand has moderated from the pandemic peak, but it hasn’t disappeared. The buyers are still out there, and if you price your house at current market value, you’ll still be able sell your house today.
Bottom Line
If you have questions about selling your house in today’s housing market, let’s connect. That way you have context around what’s happening now, so you’re up to date on what you can expect when you’re ready to move.







![Three Reasons To Buy a Home in Today’s Shifting Market [INFOGRAPHIC] | MyKCM](https://files.mykcm.com/2022/07/28132341/20220729-MEM-1046x1709.png)